Netdata Agents and Parents now have a new UI!

Checkout the release meetup video or read on to learn more about the new UI and other features in this release.
Netdata Agents and Parents now have a new UI!

Checkout the release meetup video or read on to learn more about the new UI and other features in this release.
Hey there! We're excited to share a new troubleshooting feature we have added to Netdata, the Netdata Assistant. We've built this tool to help you troubleshoot more effectively and with less stress. Let's dive in.

When it comes to monitoring IT infrastructure, the costs you see on the price tag of the tool are often just the tip of the iceberg. Below the waterline, a mass of hidden costs can lurk, which can significantly affect the total cost of ownership.

We are always trying to lower the barrier to entry when it comes to monitoring and observability and one place we have consistently witnessed some pain from users is around adopting and approaching configuration management tools and practices as your infrastructure grows and becomes more complex.
To that end, we have begun recently publishing our own little example ansible project used to maintain and manage the servers used in our public Machine Learning Demo room.
This post introduces this project as a somewhat simple example of using Ansible with Netdata. Read on to learn more, but more importantly feel free to explore the repo and see how it all hangs together.

A “Parent” is a Netdata Agent, like the ones we install on all our systems, but is configured as a central node that receives, stores and processes metrics data from other Netdata “Child” nodes in our infrastructure.
Netdata Parents are flexible. You can have one big active-active cluster of Netdata Parents, or you can spread a lot of independent Parents across the infrastructure.
This “distributed still centralized” setup provides a lot of benefits. Let’s go through them one by one in this blog post.
Another release of the Netdata Monitoring solution is here!

How does Netdata's machine learning (ML) based anomaly detection actually work? Read on to find out!
In this blog post, we will explore the importance of scalability, automation, and AI in the evolving landscape of infrastructure monitoring. We will examine how Netdata's innovative solution aligns with these emerging trends, and how it can empower organizations to effectively manage their modern IT infrastructure.

In today's fast-paced digital landscape, 24-hour operations centers play a crucial role in managing and monitoring large-scale infrastructures. These centers must be equipped with an effective monitoring solution that addresses their unique needs, enabling them to respond quickly to incidents and maintain optimal system performance. Netdata, a comprehensive monitoring solution, has been designed to meet these critical requirements with its advanced capabilities and recent enhancements.
In this article, we will explore how Netdata's powerful features can transform the way 24-hour operations centers monitor and manage their complex environments, leading to improved incident detection, faster troubleshooting, and better overall system performance.
The advent of multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud architectures has created new opportunities for organizations to leverage best-in-class features from various cloud service providers. However, these complex environments present their own unique challenges, especially when it comes to monitoring and managing performance.
Unlock the full potential of your cloud investment! Discover strategies to enhance performance and reduce costs.
Embarking on a cloud migration journey? Grasp the obstacles and arm yourself with best practices for a smooth transition. Success lies in understanding, planning, and adapting.
Unlocking the full potential of monitoring through ML integration, anomaly detection, and innovative scoring engines.
So, you think you monitor your infra?
Another release of the Netdata Monitoring solution is here!
Scalability is crucial for monitoring systems as it ensures that they can accommodate growth, maintain performance, provide flexibility, optimize costs, enhance fault tolerance, and support informed decision-making, all of which are critical for effective infrastructure management.

Netdata provides a comprehensive set of charts that can help you understand the workload, performance, utilization, saturation, latency, responsiveness, and maintenance activities of your disks. In this blog we will focus on monitoring disks as block devices, not as filesystems or mount points.

Memory-intensive applications can benefit from improved performance by using huge pages, as they can reduce TLB pressure and memory fragmentation, and lower the memory management overhead overall. Developers should consider using HugeTLBfs in their mmap() and shmget() calls to take advantage of huge pages.
Transparent Huge Pages (THP) is a Linux kernel feature that provides some of the benefits of huge pages without requiring any development effort. However, THP can cause latency in many applications. Although kernel developers are actively working to address these issues, many system administrators prefer to disable THP altogether.
Netdata can assist in determining whether THP is helpful or harmful to your applications, which can guide your decision regarding its use.

The mem.kernel chart in Netdata provides insight into the memory usage of various kernel subsystems and mechanisms. By understanding these dimensions and their technical details, you can monitor your system's kernel memory usage and identify potential issues or inefficiencies. Monitoring these dimensions can help you ensure that your system is running efficiently and provide valuable insights into the performance of your kernel and memory subsystem.


Entropy is a measure of the randomness or unpredictability of data. In the context of cryptography, entropy is used to generate random numbers or keys that are essential for secure communication and encryption. Without a good source of entropy, cryptographic protocols can become vulnerable to attacks that exploit the predictability of the generated keys.

Server uptime monitoring tracks the availability and reliability of servers within your infrastructure.

Swap memory, also known as virtual memory, is a space on a hard disk that is used to supplement the physical memory (RAM) of a computer. The swap space is used when the system runs out of physical memory, and it moves less frequently accessed data from RAM to the hard disk, freeing up space in RAM for more frequently accessed data. But should swap memory be enabled on production systems and cloud-provided virtual machines (VMs)? Let's explore the pros and cons.

Context switching is the process of switching the CPU from one process, task or thread to another. In a multitasking operating system, such as Linux, the CPU has to switch between multiple processes or threads in order to keep the system running smoothly. This is necessary because each CPU core without hyperthreading can only execute one process or thread at a time. If there are many processes or threads running simultaneously, and very few CPU cores available to handle them, the system is forced to make more context switches to balance the CPU resources among them.
Context switching is an essential function of any multitasking operating system, but it also comes at a cost. The whole process is computationally intensive, and the more context switches that occur, the slower the system becomes. This is because each context switch involves saving the current state of the CPU, loading the state of the new process or thread, and then resuming execution of the new process or thread. This takes time and consumes CPU resources, which can slow down the system.
The impact of context switching on system performance can be significant, especially in systems with many processes or threads running simultaneously.

Interrupts, softirqs, and softnet are all critical parts of the Linux kernel that can impact system performance. In this blog post, we'll explore their usefulness, and discuss how to monitor them using Netdata for both bare-metal servers and VMs.

As a system administrator, understanding how your Linux system's CPU is being utilized is crucial for identifying bottlenecks and optimizing performance. In this blog post, we'll dive deep into the world of Linux CPU consumption, load, and pressure, and discuss how to use these metrics effectively to identify issues and improve your system's performance.

The different states of system processes are essential to understanding how a computer system works. Each state represents a specific point in a process's life cycle and can impact system performance and stability.

It's becoming increasingly common to discuss the importance of scalability in monitoring solutions and how it can impact the performance and reliability of distributed systems.
Introduction to Netdata's new visualisation providing AI Insights, supporting Rapid Diagnostics.


Need to monitor a UNIX-like system, but can’t install Netdata on it? With our SNMP collector and Net-SNMP, you can get basic system information with just a bit of relatively quick and easy configuration.
The menu (on the overview or single node tab) now has an anomaly rate button built into it that, for the entire visible window or a highlighted time range, shows the maximum chart anomaly rate within each section.
Read on to learn more about this new feature!

Introducing Netdata's Demo Space, a quick and easy way to experience monitoring environments before you set them up yourself.

Hello, fellow data enthusiasts and Google Colab aficionados! Today, we're going to explore how to monitor your Google Colab instances using Netdata. Colab is a fantastic platform for running Notebooks, developing ML models, and other data science and analytics tasks. But have you ever wondered how your Colab instance is performing under the hood? That's where Netdata comes into play!
At Netdata, we’re committed to trying to make Netdata work as well as possible for our users. Sometimes though, that means changing things in ways that aren’t exactly seamless. Such a change is coming soon for users of our native DEB and RPM packages, and this blog post will explain what’s happening, why we’re doing it, and what it means for our users.
Monitor your Windows server and applications running on it with Netdata - simple, powerful and free.

We have recently extended the native machine learning (ML) based anomaly detection capabilities of Netdata to support all metrics, regardless on their collection frequency (update every).
Previously only metrics collected every second were supported, but now Netdata can run anomaly detection out of the box with zero config on metrics with any collection frequency.
This post will illustrate an example of what this means using Prometheus metrics (via the Netdata Prometheus collector) since they typically have a default collection frequency of 10 seconds.

We recently got this great feedback from a dear user in our Discord:
I would really like to use Netdata to monitor custom internal metrics that come from SQL, not a fan of having 10 diff systems doing essentially the same thing as is, Netdata is pretty much all there in that regard, just needs a few extra features.
This is great and exactly what we want, a clear problem or improvement we could make to help make that users monitoring life a little easier.
This is also where the beauty of open source comes in and being able to build on the shoulders of giants - adding such a feature turned out to be pretty easy by just extending our existing Pandas collector to support SQL queries leveraging its read_sql() capabilities.
Here is the PR that was merged a few days later.
This blog post will cover an example of using the Pandas collector to monitor some custom SQL metrics from a WordPress MySQL database.
Netdata is committed to making it simpler and easier for everyone to monitor and troubleshoot their infrastructure. With that goal in mind, we're excited to announce the launch of our new "Functions" feature, which allows Netdata Agent collectors to expose "functions" that can be executed in run-time and on-demand.
All Netdata functionality is and will be available for free forever in the Community Plan. Paid tiers include features targeted for businesses and users who would need to customise their monitoring solution with different levels of user access, extra notification mechanisms, customer support and more.
Another release of the Netdata Monitoring solution is here!

We have been busy at work under the hood of the Netdata agent to introduce new capabilities that let you extend the "training window" used by Netdata's native anomaly detection capabilities.
This blog post will discuss one of these improvements to help you reduce "false positives" by essentially extending the training window by using the new (beautifully named) number of models per dimension configuration parameter.
Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot BIND 9 using Netdata

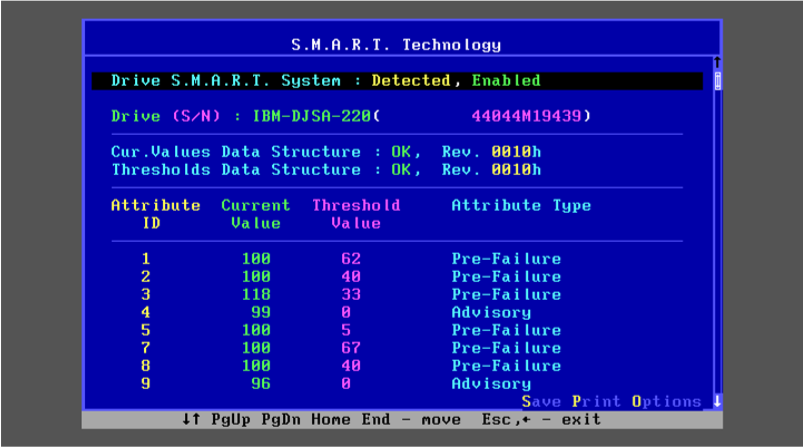
Understand what makes a storage device S.M.A.R.T and how to monitor a self monitoring component using Netdata.
Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot Memcached using Netdata

Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot NTPdaemon using Netdata

Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot MongoDB using Netdata

Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot Dovecot using Netdata

Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot CoreDNS using Netdata

Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot Dnsmasq for DHCP using Netdata

Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot Dnsmasq DNS Forwarder using Netdata

Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot systemd-logind using Netdata

Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot Postfix using Netdata

Find out how to effectively and easily monitor and troubleshoot Chrony using Netdata

Netdata v1.37.1 is a patch release to address issues discovered since v1.37.0. Refer to the v.1.37.0 release notes for the full scope of that release.
Another release of the Netdata Monitoring solution is here!
We focused on these key areas:
Infinite scalability of the Netdata Ecosystem
Default Database Tiering, offering months of data retention for typical Netdata Agent installations with default settings and years of data retention for dedicated Netdata Parents.
Overview Dashboards at Netdata Cloud got a ton of improvements to allow slicing and dicing of data directly on the UI and overcome the limitations of the web technology when thousands of charts are presented on one page.
Integration with Grafana for custom dashboards, using Netdata Cloud as an infrastructure-wide time-series data source for metrics
PostgreSQL monitoring completely rewritten offering state of the art monitoring of the database performance and health, even at the table and index level.
Find out how to monitor your Internet speed and quality and how well your ISP is performing.

FreeBSD is a high-quality, stable, and secure operating system used in a wide variety of applications, and we want to show you how monitor FreeBSD systems painlessly and effectively.

Monitoring the health and status of nodes and servers is a critical part of effective infrastructure monitoring.

Use Netdata to effectively monitor and troubleshoot the performance of NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory express) disks in your infrastructure. Preempt disk failures and take action to ensure your systems run without a glitch.

Best practices for Apache server monitoring and troubleshooting.

Web servers are among the most important components in modern IT infrastructures. They host the websites, web services, and web applications that we use on a daily basis. Social networking, media streaming, software as a service (SaaS), and other activities wouldn’t be possible without the use of web servers. And with the advent of cloud computing and the movement of more services online, web servers and their monitoring are only becoming more important. Given the extensive usage of Web servers, Sysadmins and SREs should monitor web servers as a key aspect for performance.

The health management APIs in Netdata allows teams to eliminate unnecessary alerting during scheduled maintenance, testing, auto scaling events, and instance reboots.
Monitoring indoor air quality with Airthings and Netdata. Understanding and measuring common contaminants and pollutants reduces your risk of air quality health concerns.
Monitoring KSM (Kernel Same-page Merging) performance at deduping memory shared across VMs.
How to monitor and troubleshoot Cassandra with Netdata.

Database bloat is disk space that was used by a table or index and is available for reuse by the database but has not been reclaimed. Bloat is created when deleting or updating tables and indexes. Here's how to deal with it!
What are the important Cassandra metrics to monitor and how to monitor them.
We often hear the term load used to describe the state of a server or a device, but we're here to tell you what it means, precisely, and how to monitor it.
The most important part of disk usage monitoring is to check the utilization of each filesystem and each mount point which can reveal existing or impending issues with the storage space on your infrastructure.
Redis is designed to be fast. In most cases, it is. However, there are times when Redis may be slow, due to network issues, disk latency, or other factors. When this happens, it is important to be able to detect the slow down and investigate the cause of Redis latency.
The life of a sysadmin or SRE is often difficult, but occasionally very simple things can make a huge difference. Basic monitoring of your systemd services is one of those simple things, which we sometimes overlook. The simplest question one would want to know is if the thing that’s supposed to be running is actually running at all. If you use systemd services, you can guarantee an answer to that question within minutes using Netdata.
Netdata just got a Pandas collector.
The HTTP protocol has become the de facto standard application layer protocol of the internet. From publicly available web sites and APIs to “inter-process” communications in REST based microservice architectures or large Service Oriented Architectures based on SOAP, you find HTTP being used again and again, due to its simplicity and our familiarity with it. How many protocols can you name that have memes for their status codes? Of course, such a popular protocol has endless pages written about how to properly monitor the services that rely on it, with many options specific to every use case.
DNS (Domain Name System) servers translate standard language web addresses to their actual IP addresses for network access.
High availability. This is what every monitoring tool needs to ensure that you never compromise on IT infrastructure visibility.
Most sysadmins and developers have at some point used a few of the popular Linux networking commands or their Windows equivalents to answer the common questions of host reachability - that is, whether a host or service is reachable and how fast it responds.

The open-source community is about to benefit greatly from Netdata's new Grafana data source plugin, which makes use of a powerful data collection engine.
It is sometimes easy to get lost in the mountain of metrics and infinite number of dimensions when working with an infrastructure monitoring tool. Being able to filter metrics by label and visualize only what is relevant to the current scope of monitoring &troubleshooting, becomes absolutely crucial to the success of SREs, Sysadmins and DevOps professionals.
While working on improving the Netdata PostgreSQL collector, we were monitoring our production PostgreSQL instance and something caught our attention immediately. The rows fetched ratio seemed really, really low for one particular database... there were missing indexes in PostgreSQL!


Following on from the recent launch of our Anomaly Advisor feature, and in keeping with our approach to machine learning, here is a detailed Python notebook outlining exactly how the machine learning powering the Anomaly Advisor actually works under the hood.
As of v1.35.0 the Netdata Agent can now run Metric Correlations (MC) itself. This means that, for nodes with MC enabled, the Metric Correlations feature just got a whole lot faster!
Today we are excited to launch one of our flagship ML assisted troubleshooting features in Netdata – the Anomaly Advisor.
The Anomaly Advisor builds on earlier work to introduce unsupervised anomaly detection capabilities into the Netdata Agent from v1.32.0 onwards.
CPU limits are probably the most misunderstood concept in Kubernetes CPU resources allocation and management.
Together with you, our fabulous community, Netdata is changing the way the world thinks of high fidelity monitoring - and we are gaining momentum.
There is a lot of buzz in the world of machine learning (ML) and as a layperson it can be hard to keep up with it all. Therefore, we decided to write down some of our thoughts and musings on how we are approaching ML at Netdata.